Business
2iec
Structured Writing - Simple Model

Structured Writing - Intermediate Model

Structured Writing - Advanced Model

Learner Guide
Check the Learner GuidePart 1: Business and its environment
- Enterprise
- Business structure
- Size of business
- Business objectives
- Stakeholders in a business
Chapter 1: Enterprise
- business objectives
- transformation process
- factors of production
- primary sector
- adding value
- brand
- market forces
- opportunity cost
- entrepreneur
- enterprise
- intrapreneur
Chapter 2: Business structure
- nationalisation
- privatisation
- merit goods
- unlimited liability
- company
- shareholders
- limited liability
- franchise
- co-operatives
- joint ventures
- social enterprises
Chapter 3: Size of business
- niche
- type of integration (horizontal, vertical, conglomerate diversification)
- internal and external growth
Chapter 4: Business objectives
- objective
- labour productivity
- corporate objective
- market share
- cash flow
- ethics
- social responsibility
Chapter 4: Business objectives
- mission statement
- aim
- strategy
- tactics
- target
- budgets
- ethical behaviour
Chapter 5: Stakeholders in a business
- stakeholders
- authority
- internal stakeholders
- external stakeholders
- dividends
Chapter 6: External influences on business activity
- Political and legal influences
- Social and demographic influences
- Technological influences on business activities
- Influence of competitors and suppliers
- International influences
- Environmental influences on business activity
1. Political and legal influences
- privatisation or nationalisation
- legal constraints
- conditions of work, minimum wage, ...
- competition
- ...
- health and safety laws
- ...
activity 6.1

activity 6.2

activity 6.3

activity 6.4

2. Social and demographic influences
- corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- demographic changes
- ...
3. Technological influences on business activities
- technological change
- impact on decision-making of businesses
- process of introducing technology into a business
4. Influence of competitors and suppliers (short)
- market share
- market power
- decision on pricing
- ...
5. International influences
- international trade (importance, agreements, ...)
- WTO, Free-trade blocs
- technology in international trade
- AI
- blockchain
- digital payments
- Multinational businesses
- ...
6. Environmental influences on business activity
- CSR, environment and business decisions
- environmental audits
- sustainability
- ...
analyse ...

analyse ...

Chapter 7: External economic influences on business activity
- Government support for business activity
- How governments deal with market failure
- Macroeconomic objectives of governments
- How economic objectives and performance impact business activity
- Government policies to achieve macroeconomic objectives
Government support for business activity
- Government assistance for entrepreneurs
- loan guarantee schemes
- provide information, advice, training, ...
- financing of workshops, ...
- reduce paperwork and legal formalities
- reduce corporation tax on new and small businesses
- Government assistance for all businesses
Government support for business activity
- Government assistance for entrepreneurs
- Government assistance for all businesses
- subsidies to keep prices down
- subsidies to protect employment
- grants to relocate to areas with high unemployment
- financial support for housing
Government support for business activity
advantages and disadvantages of subidies
- advantages
- avoids business failure
- keeps suppliers in business
- avoids rising imports
- disadvantages
- taxes will rise
- disincentive to be more efficient
- consumers drawn to subsidised products
How governments deal with market failure
- Examples of market failure
- external costs
- labour training
- monopoly producers
- Correcting or controlling market failure
Macroeconomic objectives of governments
- economic growth
- inflation
- unemployment
- balance of bayment
- exchange rate
How economic objectives and performance impact business activity
- Economic growth
- benefits
- causes
- business cycle
- role of recessions
- inflation and deflation
- Unemployment
How economic objectives and performance impact business activity
- Economic growth
- inflation and deflation
- causes of inflation
- impact of low inflation
- impact of high inflation
- Unemployment
How economic objectives and performance impact business activity
- Economic growth
- inflation and deflation
- Unemployment
- causes of unemployment
- cyclical unemployment
- structural unemployment
- frictional unemployment
- costs of unemployment
Government policies to achieve macroeconomic objectives
- Monetary policy
- Fiscal policy
- Supply-side policies
- Exchange rate policy
Chapter 8: Business strategy
- Business strategy : meaning and purpose
- Strategic management: meaning and purpose
- Approaches to developing business strategy
Business strategy : meaning and purpose
- Establishing business strategy
- Resources available
- Strengths of the business
- Competitive environment
- Objectives
Strategic management: meaning and purpose
- Strategic choice
- Strategic implementation
- Strategy and tactics
- The need for strategic management
Approaches to developing business strategy
- Blue ocean strategy
- Scenario planning
- SWOT analysis
- PEST analysis
- Porter's five forces analysis
- Core competencies
- The Ansoff matrix
- Force-field analysis
- Decision trees
essay questions
- Evaluate how a large supermarket company might use SWOT and PEST analysis in order to make a successful expansion overseas.
- Evaluate why a hotel business might use blue ocean strategy, rather than concentrating on red ocean strategy.
- Evaluate how a fast-food company might use Porter's Five Force analysis to identify changes to the market environment in which they operate.
essay questions
- Evaluate whether a retail clothing business without identifiable core competencies might fail in the market in your country.
- Evaluate how a wheat-farming business might use the Ansoff Matrix and decision-tree analysis to decide whether to move into chicken farming or use the land to build and rent holiday accommodation to tourists.
Part 2: Human resource management
- Human resource management
- Motivation
- Management
Chapter 10: Human resource management
- human resource management (HRM)
- delayering
- teamworking
- workforce plan (or human resource plan)
- labour turnover
- recruitment and selection
- job descriptions
- person specifications (or job specifications)
- employment contract
Chapter 10: Human resource management
- business culture
- dismissal
- redundancies
- employee welfare
- employee morale
- work-life balance
- diversity
- equality
Chapter 10: Human resource management
- training
- development
- delegation
- intrapreneurship
- multi-skilling
- trade union
- collective bargaining
Chapter 10: Human resource management
\[\begin{aligned} \text{turnover} & = \frac{ \text{number of staff leaving during the year} }{ \text{average number of staff} } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 11: Motivation
- motivation
- absenteeism
- human needs
- schools of thought
- piece-rate
- division of labour
- hierarchy of needs
- hygiene factors ( or maintenance factors)
- motivators
Chapter 11: Motivation
- performance-related pay (PRP)
- variable pay
- fringe benefits (or perks)
- job redesign
- job enrichment (or vertical loading)
- job enlargement (or horizontal loading)
- job rotation
- empowerment
- job design
- employee participation
Chapter 12: Management
- leadership
- management
- autocratic management (or authoritarian management)
- paternalistic management
- democratic management (or participative management)
- laissez-faire management
Part 3: Marketing
- The nature of marketing
- Market research
- The marketing mix - product and price
- The marketing mix - promotion and place
Chapter 17: The nature of marketing
- marketing
- marketing objective
- corporate objective
- marketing strategy
- business-to-consumer marketing (B2C)
- business-to-business marketing (B2B)
- market size
Chapter 17: The nature of marketing
- market growth
- unique selling point (USP)
- niche marketing
- market segment
- mass marketing
- customer-relationship marketing (CRM)
- customer retention
Chapter 17: The nature of marketing
\[\begin{aligned} \text{market share} & = \frac{ \text{sales of a business (or product)} }{ \text{total market sales} } \times 100 \\ \\ \text{market growth} & = \frac{ \text{(market sales)}_{ \text{this year} } - \text{(market sales)}_{ \text{last year} } }{ \text{market sales}_{ \text{last year} } } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 18: Market research
- market research
- primary market research
- focus group
- secondary market research
- sample
- validity of market research
- reliability of market research
Chapter 18: Market research
\[\begin{aligned} \text{market growth} & = \frac{ \text{change in market size} }{ \text{original market size} } \times 100 \\ \\ \text{market share of business} & = \frac{ \text{sales by the business} }{ \text{total market sales} } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 19: The marketing mix - product and price
- marketing mix
- products
- tangible attributes
- intangible aspects
- product differentiation
- product portfolio analysis
- product life cycle
- extension strategy
- product portfolio analysis (PPA)
Chapter 19: The marketing mix - product and price
- Boston Matrix
- competitive pricing
- penetration pricing
- price skimming
- price discrimination
- dynamic pricing
- cost-based pricing
- psychological pricing
- promotional mix
Chapter 20: The marketing mix - promotion and place
- digital promotion
- click-through rate (CTR)
- marketing expenditure budget
- distribution channel
- distribution outlet
The Economics of Aldi
strategies that Aldi uses to maintain low prices and attract customers
The Economics of Aldi
discuss the following items
- Store Layout and Size
- Limited Product Range and Simplified Operations
- Cost-Cutting Measures
- Marketing and Customer Perception
- Known Value Items
- Private Label Products
- Recession and Growth
- Expansion and Competition
- Target Audience
Part 4: Operations management
- The nature of operations
- Inventory management
- Capacity utilisation and outsourcing
Chapter 23: The nature of operations
- output
- inventory
- operations mangement
- productivity
- sustainable
- capital-intensive
- labour-intensive
- marketing function
$\longrightarrow$ identify opportunities within a market - operations function
$\longrightarrow$ deliver as effectively as possible
effective operations
- means the business ...
- ... is meeting its operational targets
efficient operations
- produce and deliver products ...
- ... in a cost-efficient manner
consequences of poor operations
- mistakes are being made during production
- items will have to be replaced
- products have to be recalled
- damages have to be paid
output
- the total amount produced ...
- ... in a given time period
different forms of the transformation process
involves changing the ...- ... characteristics of
- materials
- information
- customers
- ... location of materials and information
- ... ownership of materials
inventory
- refers to the stocks held in a business ...
- ... such as materials ...
- ... and semi-finished goods
operations mangement
- overseeing ...
- ... the planning, coordination and control
- ... of the transformation process, ...
- ... turning resources (inputs) into outputs.
factors of production
- land
- labour
- capital
- enterprise
labour productivity
\[\begin{aligned} \text{labour productivity} & = \frac{ \text{total output} }{ \text{number of employees} } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
productivity
- measures the output per hour, ...
- ... per person ...
- ... or per machine.
sustainable activities
- activities that meet the needs of ...
- ... the business or of society ...
- ... without compromising on the ability ...
- ... to meet future needs.
capital-intensive production
- production where there is ...
- ... a high proportion of capital ...
- ... used relative to ...
- ... other factors of production.
labour-intensive production
- production where there is ...
- ... a relatively high proportion ...
- ... of labour used relative to ...
- ... other factors of production.
production process
- factors of production
- land
- labour
- capital
- enterprise
- stages of production :
input $\longrightarrow$ production process $\longrightarrow$ output - operations can increase the added value
operations can increase added value by managing
- efficiency of production
- quality of goods & services
- flexibility & innovation of processes
- design of the product
- efficiency of operations
- effective branding of the product
$\longrightarrow$ production costs $\downarrow$
$\longrightarrow$ quality of goods $\uparrow$
$\longrightarrow$ flexibility of production $\uparrow$
productivity
- high productivity $\longrightarrow$ competitiveness $\uparrow$
- measuring productivity
\[\begin{aligned} \text{labour productivity} & = \frac{ \text{total output} }{ \text{number of employees} } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
productivity can be increased by
- improving training of employees
$\longrightarrow$ skill level $\uparrow$ - improving worker motivation
- purchasing new technologies
- guaranteeing more efficient management
high productivity : no guarantee for success!
- how popular is the product?
- highly productive workers $\longrightarrow$ wages $\uparrow$
- resistence by workers to measures
- culture of management
- efficiency $\neq$ effectiveness
sustainable operations
- energy use $\downarrow$ & carbon emissions $\downarrow$
- use of non-biodegradable material $\downarrow$
- use of recycled material $\uparrow$
- products that is recyclable
labour intensive operations
- advantages
- interesting job
- low reliance on machines
- meet customer requirement
- disadvantages
- low output
- skilled labour required
- quality not always uniform
labour intensive operations

capital intensive operations
- advantages
- economies of scale
- consistent quality
- low unit cost
- mass production
- disadvantages
- high fixed costs
- high maintenance costs
- keep up with technology changes
capital intensive operations

types of operations methods
- job production : one-off production
- batch production : move from one stage of process to another
- flow production : large scale production
- mass customisation : large scale production with flexibility
job production

batch production

flow production

factors influencing the choice of production method
- size of market
- availability of capital
- availability of other resources
- unskilled workers $\rightarrow$ mass production
- flat area land $\rightarrow$ mass production
- customer requirements
Chapter 24: Inventory management
- supply chain
- supply chain management
- lean production
operations efficiency & inventory
- holding cost $\leftrightarrow$ cost of running out of supplies
- reasons for holding inventory
- raw materials & components (as input)
- work in progress
- finished goods (until being sold)
operations efficiency & inventory
- problems rising from insufficient inventory
- unforseen changes in demand
- obsolete inventories
- inventory wastage
- opportunity costs
- late deliveries
cost & benefit of holding inventory
- cost of holding inventory
- opportunity cost
- storage cost
- wastage & obsolescence
- benefit of holding inventory
- risk of lost sales $\downarrow$
- allows continuous production
- need for special orders from suppliers $\downarrow$
total inventory-holding cost
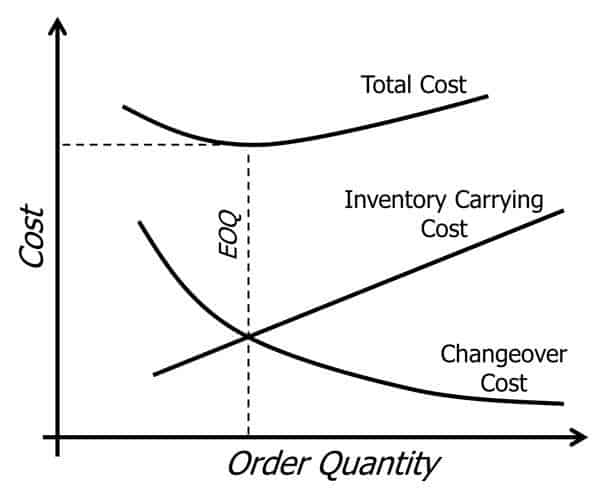
- economic order quantity (EOQ)
inventory control chart
- monitor a firm's inventory position
- helps to determine the
- appropriate order time and
- order quantity
- key features of inventory control chart
- buffer inventories
- maximum inventory level
- re-order quantity
- lead time
- re-order level
inventory control chart

supply chain management
- goal of supply chain management
- minimize costs and
- improve customer service
- reduce time to convert raw material into completed product
- benefits of supply chain management
- improves customer service
- reduces operating costs
- umproves profitability
just-in-time model (applied to Toyota)

just-in-time
- advantages
- capital invested in inventory $\downarrow$
- storage cost $\downarrow$
- risk of obsolescence of inventory $\downarrow$
- multi-skilled and adaptable staff
- disadvantages
- delay in supplies $\rightarrow$ production delays
- delivery costs
- many small orders $\rightarrow$ administration cost
- reputation may depend on outside firms
just-in-time model and COVID

source: Supply chains: companies shift from 'just in time' to 'just in case' (FT)
conditions for successful JIT
- good supplier relationships
- skilled and flexible production staff
- flexible machinery
- accurate demand forecasts
- modern IT equipment
- excellent employer-employee relationships
Chapter 25: Capacity utilisation and outsourcing
- capacity
- factors of production
- capacity utilisation
- capacity under-utilisation
- rationalisation
- subcontracting
- outsourcing
Chapter 25: Capacity utilisation and outsourcing
\[\begin{aligned} \text{per cent capacity} & = \frac{ \text{existing output}_{ \text{over a given time period} } }{ \text{maximum possible output}_{ \text{over a given time period} } } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
Part 5: Finance and accounting
- Business finance
- Forecasting and managing cash flows
- Costs
- Budgets
Chapter 29: Business finance
- asset
- capital
- non-current assets
- short-term sources of finance
- long-term sources of finance
- insolvency
- liabilities
- bankruptcy
- liquidation
Chapter 29: Business finance
- administration
- working capital
- current assets
- trade payables
- trade receivables
- revenue expenditure
- capital expenditure
- statement of financial position
- income statement
asset
- an item owned by a business ...
- ... that can generate an income for the enterprise
- Examples:
- supply of raw material
- machinery
capital
- money invested into a business ...
- ... either by its owners or by other organisations
- Examples:
- money
- machinery
- building
non-current assets
- assets ...
- ... that a business expects to hold for one year or more
- Examples:
- property
- vehicles
sources of finance
- short-term sources of finance : needed for limited period of time (< 1 year)
- long-term sources of finance : needed over a long period of time (> 1 year)
insolvency
- debts (of the business) > assets (available)
- business is unable to pay its debts
liabilities
- money owned by a business ...
- ... to individuals, suppliers, banks, ...
working capital
- money used to pay for day-to-day expenses ...
- ... so the business can keep operating
current assets
- are items owned by a business ...
- ... that can be readily turned into cash
- Examples :
- cash in bank
- trade and other receivables due to settle their accounts soon
- inventories - raw materials and components
current liabilities
- debts payable in short term
- debts repayable to the bank (i.e. overdraft)
- trade and other payables who expect to be paid in the near future
- tax due to authorities
working capital
\[\begin{aligned} \text{working capital} & = \text{current assets} - \text{current liabilities} \end{aligned} \]
bankruptcy
- when an individual, a sole trader or a partnership ...
- ... is judged unable to pay its debts ...
- ... by a court of law
liquidation
- is the dissolution of a company ...
- ... by selling its assets to settle its liabilities
administration
- is a process available to a company ...
- ... to protect itself ...
- ... while it attempts to pay its debts ...
- ... and escape insolvency
trade payables
- is the amount of money ...
- ... owed by a business to its suppliers ...
- ... for goods and services ...
- ... that have been received ...
- ... but which have not been paid for
trade receivables
- is the amount of money ...
- ... owed by a business' customer ...
- ... for products ...
- ... that have been supplied ...
- ... but for which payment has not yet been made
revenue expenditure
- refers to the purchase of items ...
- ... that will be used up within a short space of time
- Examples :
- fuel
- raw materials
capital expenditure
- is the spending by a business ...
- ... on non-current assets
- Examples :
- premises
- production equipment
- vehicles
statement of financial position (balance-sheet)
- is a financial statement ...
- ... that records the assets (possessions) and liabilities (debts) of a business ...
- ... on a particular day ...
- ... at the end of an accounting period
- Example : Luxair (p.56-59)
income statement
- is a financial statement ...
- ... showing a business' sales revenue ...
- ... over a trading period ...
- ... and all the relevant costs incurred to generate that revenue
- Example : Luxair (p.60)
income statement
- is a financial statement ...
- ... showing a business' sales revenue ...
- ... over a trading period ...
- ... and all the relevant costs incurred to generate that revenue
- Example : Luxair (p.60)
Classroom activity
- Read Mobile Phone extract (p.488)
- Analyse the likely increase in working capital from this expansion.
- Discuss how inventories, trade payables and trade receivables could be managed to reduce the need to increse working capital.
- see Learner Guide for the command words
Homework
- Read chapter 29 for next week.
- Revise using the Exam-Style Questions
need for business finance
- why?
start-up capital, working capital, R&D, buy other companies, survival of company - short-term vs. long-term need
buy inventory before busiest months (ST), buy equipment and buildings (LT) - cash $\neq$ profit
cash is needed in the short-run, profit can wait for the long-run
need for business finance
- administration business fails due to a lack of finance
- bankruptcy accountants are appointed to keep the business operational and find a buyer for it - if they fail we have bankruptcy
- liquidation a legal process will begin that will liquidate the assets of the business
working capital
Chapter 30: Forecasting and managing cash flows
- cash flow
- insolvent
- cash flow forecast
- cash inflow
- cash outflow
- net cash flow
Chapter 30: Forecasting and managing cash flows
- opening cash balance
- closing cash balance
- credit control
- bad debt
- overtrading
- decision-making
cash flow
- the sum of ...
- ... cash payments ...
- ... to a business ...
- ... less ...
- ... the sum of ...
- ... cash payments ...
- ... from the business
$ \text{net cash} = \text{total cash inflows} - \text{total cash outflows} $
insolvent
- when a business ...
- ... cannot meet ...
- ... its short-term debts
cash flow forecast
- an estimate ...
- ... of the future ...
- ... cash inflows and outflows ...
- ... of a business
- cash inflow: cash payments into a business
- cash outflow: cash payments out of a business
cash inflows examples
- owner's own capital
- bank loan
- customer's cash purchases
- trade receivables
cash outflows examples
- lease payments
- rent payment
- electricity, water, phone, ... bills
- wage payments
- cost of materials
- payments to suppliers
cash flow forecast

net cash flow
- estimated difference between ...
- ... cash inflows and cash outflows ...
- ... for the period (i.e. month)
$ \text{net cash flow} = \text{total cash inflows} \\ \hspace{8cm} - \text{total cash outflows} $
in a given time period (for example, month)
opening cash balance
- cash held by ...
- ... the business ...
- ... at the start of the month
closing cash balance
- cash held by ...
- ... the business ...
- ... at the end of the month
closing cash and opening cash balance
$\text{(closing cash)}_{\text{february}} = \text{(opening cash)}_{ \text{march} }$
cash flow forecast
 $\text{closing cash balance}$
$\text{closing cash balance}$ $=$
$ \text{opening cash balance} + ( \text{cash inflows} - \text{cash outflows} ) $
application: cash flow forecast

application: cash flow forecast
- Draw up the revised cash flow forecast for December, assuming
- cash sales are forecast to be 300 USD higher
- payments to bank interests are forecast to be 150 USD higher
- wages are forecast to be 2000 USD higher
- Recalculate the closing cash balance for December.
credit control
- monitoring of debts ...
- ... to ensure that ...
- ... credit periods ...
- ... are not exceeded
bad debt
- unpaid customers' bills ...
- ... that are now very unlikely ...
- ... to ever be paid
overtrading
- expanding a business rapidly ...
- ... without obtaining ...
- ... all of the necessary finance ...
- ... resulting in a cash flow shortage
decision-making
Chapter 31: Costs
- break-even point
- cost centre
- direct costs
- indirect costs
- fixed costs
- variable costs
- total costs
- profit centre
Chapter 31: Costs
- average cost
- full costing
- contribution costing
- marginal cost
- break-even analysis
- margin of safety
- contribution per unit
Chapter 31: Costs
- costs
- revenue
- direct costs
- indirect costs
- full costing
- contribution
- break-even
- profits
Chapter 31: Costs
- contribution costing
- average costs
- marginal costs
- cost-plus pricing
- contribution pricing
- special-order decisions
- margin of safety
costs
- expenses ...
- ... that a business has to pay ...
- ... to engage in its trading activities
revenue
- income a business receives ...
- ... from selling ...
- ... its goods and services
$ \text{revenue} = \text{quantity sold} \times \text{average selling price} $
profit (or loss)
$ \text{profit (or loss)} = \text{total revenue} - \text{total cost} $- Profit if $\text{TR} > \text{TC}$
- Loss if $\text{TR} < \text{TC}$
- Break-even if $\text{TR} = \text{TC}$
break-even point
- the level of output at which ...
- ... total costs equal total revenue ...
- ... when neither a profit ...
- ... nor a loss is made
cost centre
- the section of a business ...
- ... such as a department or a product ...
- ... that incurs the costs
direct costs
- these costs can be clearly identified ...
- ... with each unit of production ...
- ... and can be allocated ...
- ... to a cost centre
- Examples: automobile industry
- direct materials: sheet steel, engine parts
- direct labour: wages paid to employees on production line
indirect costs
- costs that cannot be identified ...
- ... with a unit of production ...
- ... or allocated accurately ...
- ... to a cost centre
- Examples: automobile industry
- indirect labour costs: management salaries, wages paid to security staff
- other indirect costs: administration, distribution
contribution
- difference between ... ...
- ... sales revenue and ...
- ... variable costs of production
contribution
fixed costs
- costs that do not vary ...
- ... with output ...
- ... in the short run

Decomposing total costs as fixed costs plus variable costs.
variable costs
- costs that vary ...
- ... with output

Decomposing total costs as fixed costs plus variable costs.
total costs
- variable cost ...
- ... plus fixed cost

Decomposing total costs as fixed costs plus variable costs.
profit centre
- a section of a business ...
- ... to which both costs and revenues ...
- ... can be allocated ...
- ... so profit can be calculated
average cost
- total cost ...
- ... divided by the ...
- ... number of units produced
full costing
- a method of costing in which all ...
- ... indirect and direct costs ...
- ... are allocated to the ...
- ... products, services or divisions ...
- ... of a business
contribution costing
- costing method ...
- ... that allocates only direct costs ...
- ... to cost centres and profit centres ...
- ... not overhead costs
cost centre
- in a manufacturing business
- products
- departments
- factories
- in a hotel
- restaurant
- reception
- room letting
- in a school
- subject departments
profit centre
- branches of a chain of shops
- departments of a department store
- products in a portfolio of a firm
overhead (indirect expenses)
- production overheads
- rent
- depreciation
- selling and distribution overheads
- warehouse
- packing and distribution costs
- administration overheads
- office rent
- clerical salaries
- finance overheads
- interest on loans
marginal cost
- the additional cost of producing ...
- ... one more unit of output
break-even analysis
- uses cost and revenue data ...
- ... to determine the break-even point ...
- ... of production

A standard break-even analysis chart
break-even output
$ \text{break-even output} = \frac{ \text{fixed costs} }{ \text{contribution per unit} } $
$ \text{where} $
$ \scriptsize{\text{contribution per unit} = \text{selling price per unit} - \text{variable cost per unit}} $
margin of safety
- the amount by which ...
- ... the current output level ...
- ... exceeds ...
- ... the break-even level of output

margin of safety
$\text{margin of safety (%)} = \frac{ \text{current level of sales} - \text{break-even output} }{ \text{current level of sales} } \times 100 $
Interpretation: A business could lose just over x % of its sales before it found itself in a break-even position.
margin of safety
contribution per unit
- the price of a product ...
- ... less ...
- ... the direct (variable) costs ...
- ... of producing it
cost-plus pricing
- the process of establishing ...
- ... the price of a product ...
- ... by calculating its cost of production ...
- ... and then adding an amount ...
- ... which is profit
contribution pricing
- based on the notion ...
- ... that any price set that is higher than ...
- ... the variable cost of producing a product ...
- ... is making a payment towards fixed costs
class-room activity: data response question
- Midtown Imperial Hotel (p.530)
- Cosmic Cases (p.531)
- Gowri's Pottery (p.531)
- Abbey Restaurant (p.532)
Chapter 31: Costs
\[\begin{aligned} \text{profit (or loss)} & = \text{total revenue} - \text{total costs} \\ \\ \text{total cost of production} & = \text{direct costs} + \text{indirect costs} \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 31: Costs
\[\begin{aligned} \text{contribution per unit} & = \text{selling price of one unit of output} \\ & \ \ \ \ \ \ + \text{variable costs of producing that unit} \\ \text{or} \\ \text{contribution} & = \text{revenue} + \text{variable costs} \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 31: Costs
\[\begin{aligned} \text{break-even output} & = \frac{ \text{fixed costs} }{ \text{selling price per unit} - \text{variable cost per unit} } \\ \text{or} \\ \text{break-even output} & = \frac{ \text{fixed costs} }{ \text{contribution per unit} } \end{aligned} \]
Chapter 31: Costs
\[\begin{aligned} \text{margin of safety} & = \frac{ \text{current level of sales} - \text{break-even output} }{ \text{current level of sales} } \times 100 \end{aligned} \]
What does the 'margin of safety' in budgeting refer to?
How is 'contribution per unit' calculated in cost accounting?
What does break-even analysis primarily determine?
What does 'marginal cost' refer to in economics?
What is the primary focus of contribution costing in management accounting?
What is a key characteristic of full costing?
What does 'average cost' represent in economics?
What is a 'profit centre' in a business organization?
What is a 'cost centre' in a business organization?
What is the main difference between direct and indirect costs in business?
How are fixed costs, variable costs, and total costs related in business?
Chapter 32: Budgets
- incremental budgeting
- flexible budget
- budget holder
- zero budgets
Chapter 32: Budgets
- budgeting
- budget holder
- variance analysis
- delegated budgets
- incremental budgeting
- zero budgeting
- favourable variance
- flexible budgeting
- adverse variance
budgeting
- planning future activities ...
- ... by establishing ...
- ... performance targets ...
- ... especially financial ones
budget holder
- the individual ...
- ... responsible for ...
- ... initial setting and achievement ...
- ... of a budget
variance analysis
- calculation of ...
- ... the differences between ...
- ... budgets and actual figures ...
- ... and analysis of the reasons ...
- ... for such differences
delegated budgets
- budgets for which ...
- ... junior managers ...
- ... have been given ...
- ... some authority ...
- ... for setting and achieving
incremental budgeting
- uses last year's budget ...
- ... as a basis ...
- ... and an adjustment is made ...
- ... for the coming year
zero budgeting
- sets budgets to zero ...
- ... each year and ...
- ... budget holders ...
- ... have to argue their case ...
- ... for target levels ...
- ... and to receive any finance
favourable variance
- a change from the budget ...
- ... that leads to
- ... higher than planned profit
flexible budgeting
- cost budgets ...
- ... for each expense ...
- ... are allowed to vary ...
- ... if sales or output ...
- ... vary from budgeted levels
adverse variance
- a change from ...
- ... the budget that leads ...
- ... to lower than planned profit
Collaborative reading
- The measurement of performance
- Benefits of using budgets
- Potential drawbacks of using budgets
- Key features of effective budgeting
- Setting and using budgets
- Variance analysis
The measurement of performance
- actual performance vs. pre-set targets
- non-financial targets
- financial targets
benefits of using budgets
- planning
- allocating resources
- setting targets
- coordination
- controlling and monitoring a business
- measuring and assessing performance
potential drawbacks of using budgets
- lack of flexibility
- focus on the short term
- unnecessary spending
- training on budgets
- budgets for new projects
key features of effective budgeting
- budget: not a forecast but a plan
- outcome must be measurable
- coordination between departments
- participation (delegated budgets)
- identify successful/unsuccessful managers of cost or profit centres
setting and using budgets
- incremental budgeting
- zero budgeting
- flexible budgeting
variance analysis
Definition: A variance is the difference between a budget and the actual figures
- measuring performance
- making realistic budgets in the future
- taking better decisions
- assessing performances in an objective way
- causes of
- adverse variances vs.
- causes of favourable variances
Variance Analysis Example
| Item | Budgeted | Actual | Variance | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $100,000 | $120,000 | $20,000 | Favorable |
| Cost of Goods Sold | $50,000 | $55,000 | -$5,000 | Adverse |
| Operating Expenses | $20,000 | $18,000 | $2,000 | Favorable |
general tips
If you have case studies, here is what you could do:
- Do some background research of the business or the brand.
- Identify the relevant theory by finding the chapter, section, ... in your textbook.
- Adapt the elements from the theory to your case study: What is the source of the problem that is discussed in the case study?
- Propose a solution based on the issue that you have identified in the previous step.
Which of the following is true about zero-based budgeting?
What is the primary purpose of variance analysis in budgeting?
What is the main advantage of using delegated budgets within an organization?
What is a key feature of flexible budgeting?
What is a characteristic feature of incremental budgeting?
2iec Exam Overview
- Paper 1 - 40 marks - 75 minutes
- Paper 2 - 60 marks - 90 minutes
2iec Exam Overview
- Paper 1 - 40 marks - 75 minutes
- Section A : short questions
(2, 3, and 5 marks) - Section B : analyse (8 marks) and evaluate (12 marks)
- Paper 2 - 60 marks - 90 minutes
2iec Exam Overview
- Paper 1 - 40 marks - 75 minutes
- Paper 2 - 60 marks - 90 minutes
- contains two extracts
- 2 $\times$ four short questions
(1, and 3 marks) - 2 $\times$ analyse (8 marks) and evaluate (12 marks)
Paper 1
- Define (KN,UN) - 2 marks
- Explain (KN,UN,APP) - 3 marks
- Analyse (KN,UN,APP,AN) - 5 marks
- Analyse (KN,UN,APP,AN) - 8 marks
- Evaluate (KN,UN,APP,AN,EV) - 12 marks
Paper 2
- Identify (KN,UN) - 1 marks
- Explain (KN,UN,APP) - 3 marks
- Calculate (KN,UN,APP) - 3 marks
- Analyse (KN,UN,APP,AN) - 8 marks
- Evaluate (KN,UN,APP,AN,EV) - 12 marks
Formulae
- revenue (sales or turnover) =
selling price per unit $\times$ number of units sold - variable costs (total variable costs) =
variable cost per unit $\times$ number of units sold - total costs =
fixed costs $+$ variable costs - profit =
total revenue $-$ total costs OR
total contribution $-$ fixed costs
Formulae
- growth rate (%)
$ \frac{ \text{ starting value } - \text{ end value } }{ \text{ end value } } \times $ 100
Formulae
- market capitalisation of a business =
number of issued shares $\times$ current share price
Formulae
- expected value of a decision with two possible outcomes eg. A & B =
[pay-off of A $\times$ probability of A]
$+$
[pay-off of B $\times$ probability of B] - net gain =
expected value $-$ initial cost of decision
Formulae
- market growth (%) =
$\frac{ \text{change in the size of the market over a period} }{ \text{original size of the market} }$ $\times$ 100
Formulae
- market share =
$\frac{ {\text{ sales of business }} }{ \text{ sales of industry } } \times$ 100
Formulae
- market share (%) =
$\frac{ \text{ sales of one product OR brand OR business } }{ \text{ total sales in the market } }$ $\times$ 100
Formulae
- added value =
selling price
$-$
costs of raw materials
Formulae
- added value =
sales revenue
$-$
costs of bought-in goods and services
Formulae
- labour productivity =
$\frac{ {\text{ output over a time period }} }{ \text{ number of employees } }$
Formulae
- unit costs (average costs) =
$\frac{ {\text{ total costs }} }{ \text{ number of units of output } }$
Formulae
- income elasticity of demand =
$\frac{ {\text{ % change in demand }} }{ \text{ % change in income } }$
- if income elasticity $\lt$ 0 then inferior good
- if income elasticity $>$ 0 (large value) then branded good
- if income elasticity $>$ 0 (low value) then necessity
Formulae
- capacity utilisation (%) =
$\frac{ {\text{ actual output }} }{ \text{ maximum possible output } } \times $ 100
Formulae
- unit cost =
$\frac{ {\text{ total cost }} }{ \text{ number of units } } $
Formulae
- return on investment (%) =
$\frac{ {\text{ profit from the investment (£) }} }{ \text{ cost of the investment (£) } } \times $ 100
Formulae
- gross profit =
revenue $-$ cost of sales - profit from operations (operating profit) =
gross profit $-$ operating expenses - profit for year =
operating profit
$+$ profit from other activities
$-$ net finance costs
$-$ tax
Formulae
- gross profit margin (%) =
$ \frac{ \text{ gross profit } }{ \text{ revenue } } \times $ 100
- profit from operations margin (%) (operating profit margin) =
$ \frac{ \text{ operating profit } }{ \text{ revenue } } \times $ 100
Formulae
- profit for year margin (%)
$ \frac{ \text{ profit for year } }{ \text{ revenue } } \times $ 100
Formulae
- variance =
budgeted figure $-$ actual figure
Formulae
- contribution per unit =
selling price $-$ variable costs per unit - total contribution =
contribution per unit $\times$ units sold
OR
- total contribution =
total revenue $-$ total variable costs
Formulae
- break-even output =
$\frac{ \text{ fixed costs } }{ \text{ contribution per unit } }$
- margin of safety =
actual level of output
$-$ break-even level of output
Formulae
- labour productivity =
$\frac{ \text{ total output in time period } }{ \text{ total staff employed } } $
Formulae
- absenteeism (%) =
$\frac{ \text{ number of staff absent } }{ \text{ total number of staff} } \times $ 100
Formulae
- labour turnover =
$\frac{ \text{ number of staff leaving (leaving in 1 year) } }{ \text{ number of staff employed by the business } } \times$ 100
Formulae
- employee costs as percentage of turnover =
$\frac{ \text{ employee costs } }{ \text{ turnover } } \times$ 100
Formulae
- labour cost per unit =
$\frac{ \text{ labour costs } }{ \text{ units of output } } $
Formulae
- return on capital employed (ROCE)(%) =
$\frac{ \text{ operating profit } }{ \text{ total equity + non-current liabilities } } \times $ 100
where
$ \text{total equity} + \text{non-current liabilities} $
$= \text{capital employed}$
Formulae
- current ratio =
$\frac{ \text{ current assets } }{ \text{ current liabilities } } $
Formulae
- gearing (%) =
$\frac{ \text{ non-current liabilities } }{ \text{ total equity + non-current liabilities } } \times $ 100
where
$\text{total equity} + \text{non-current liabilities}$
$ = \text{capital employed}$
Formulae
- payables days =
$\frac{ \text{ payables } }{ \text{ cost of sales } } \times$ 365
Formulae
- receivables days =
$\frac{ \text{ receivables } }{ \text{ revenue } } \times$ 365
Formulae
- inventory turnover =
$\frac{ \text{ cost of sales } }{ \text{ average inventories held } } $
Formulae
- average rate of return (%) =
$\frac{ \text{ average annual return (£) } }{ \text{ initial cost of project (£) } } \times$ 100
Sample answers
Sharing the Future (NHK)
Sharing the Future : Creating the future together. Inspiring stories of projects by Japanese people working with communities in developing countries with new ideas and efforts to help solve issues.
The Rise and Fall of Nokia Mobile
The Rise And Fall Of Nokia Mobile : Once upon a time there was a large Finnish company that manufactured the world's best and most innovative mobile phones. Nokia's annual budget was larger than that of the government of Finland and everyone who worked there shared in the windfall. But global domination cost the company its pioneering spirit and quantity gradually took over from quality, with new phone models being churned out by the dozen. Market share eroded, until in 2016, mobile phone production in Finland ceased.
The Rise and Fall of Nokia is a wry morality tale for our times, told by those that lived and worked through the rollercoaster years in a company that dominated a nation.
essay-style questions (s23)
inventory, supply chain management, operations (s23_11)
- Analyse two benefits to a business of holding high levels of inventory. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether supply chain management is the most important operational activity to the success of a manufacturer of electric cars. [12 marks]
SMART objectives, ethics, human resource management (s23_11)
- Analyse two reasons why a business should set SMART objectives. [8 marks]
- 'Ethics should always influence the human resource management (HRM) activities of a
mining business.'
Evaluate this view. [12 marks]
source of finance, working capital (s23_12)
- Analyse two benefits to a business of government grants as a source of finance. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether the most likely reason for the failure of a small retailer is poor management of its working capital. [12 marks]
unique selling point, marketing (s23_12)
- Analyse two benefits to a business of having a product with a unique selling point (USP). [8 marks]
- 'Marketing is the most important factor that will affect the success of a new coffee shop.'
Evaluate this view. [12 marks]
cash flow forecast, break-even analysis (s23_13)
- Analyse two purposes of a cash flow forecast for a business. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether break-even analysis is the most important finance activity for a new manufacturer of bicycles. [12 marks]
external recruitment, motivated workforce (s23_13)
- Analyse two benefits to a business of using external recruitment to employ a manager. [8 marks]
- 'A motivated workforce is the most important factor for the success of a low-price airline.'
Evaluate this view. [12 marks]
case study (s23)
bank overdraft, marketing mix (extract and s23_21)
- Analyse one advantage and one disadvantage to GR of using a bank overdraft. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether price or promotion is the most important element of GR's marketing mix. [12 marks]
motivation, operations (extract and s23_21)
- Analyse two ways DC can motivate young people to work on its farms. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether DC should grow its operations by opening its new cocoa processing factory. [12 marks]
training, cost information (extract and s23_22)
- Analyse two benefits to OFD of offering induction training to all employees. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether Markus needs accurate cost information before setting up OFD. [12 marks]
growth, marketing mix, product life cycle (extract and s23_22)
- Analyse one advantage and one disadvantage to MXB of growing by launching a new product range of electric scooters. [8 marks]
- Evaluate how MXB can change its marketing mix to extend the product life cycle of its range of mountain bikes. [12 marks]
costs, batch production, mass customisation (extract and s23_23)
- Analyse two impacts on FM's costs if it enters international markets. [8 marks]
- Evaluate the impact on FM's stakeholders of a change from batch production to mass customisation. [12 marks]
sources of finance, management style (extract and s23_23)
- Analyse two sources of finance GD could use to open its new shop. [8 marks]
- Evaluate whether Steve's management style will contribute to GD's future success. [12 marks]
sample student answers (not Cambridge!)
cost competitiveness, differentiation, Porter's theory of competitive advantage (student answer)
- Nike is aiming to achieve competitive advantage in the global sports footwear
market. In order to do this Nike could focus on cost competitiveness or
differentiation.
Evaluate these two options and recommend which one is most suitable for Nike to maintain its global competitiveness. [20 marks]
cash flow, profit, internal and external sources of finance (student answer)
- Liz and Les have set themselves the objective of managing Bluebells’ finances more
effectively. They are considering whether to focus more on improving cash flow or
increasing profit.
Evaluate these two options and recommend which one is more suitable for Liz and Les to achieve this objective. [20 marks]
organsational structure, flexible working practice, motivation, customer service, costs, profits (student answer)
- Starbucks aims to improve employer-employee relations in its USA stores. To do this,
Starbucks could either focus on changing its organisational structure, or extend its
flexible working practices for employees.
Evaluate these two options and recommend which one is the most suitable for Starbucks to improve its employer-employee relations. [20 marks]
global niche market, global mass market (student answer)
- Haier is aiming to continue its global expansion in the white goods market. It could
do this by focusing on either global niche markets or global mass markets for
white goods.
Evaluate these two options and recommend which approach is most suitable for Haier. [20 marks]
profitability (student answer)
- VW's new Chief Executive has been given the aim of increasing the company's
profitability. The two options VW is considering are to develop a new range
of self-driving cars or to improve productivity.
Evaluate these two options and recommend which is most suitable to achieve the aim of increasing profitability, for a business such as VW. [20 marks]
general exam tips
general tips
- it is good practice to show knowledge of key terms in questions by defining them at the start of a response (this is not the only approach to gaining the Knowledge mark)
- it is not always necessary to write lots and fill all lines available - stay focused
- make sure to link each sentence and paragraph back to the question
- makes extensive use of the extract and context
- read all the data in an extract, including any footnotes or additional information - this is usually included to make the information as accurate as possible
- to write the best answers possible, link theoretical knowledge to the global context
general tips
- response can be too long - you should aim to write concise responses in order to free up more time for the other questions
- fewer arguments that are well developed and consistently supported by the context will enable candidates to access the higher levels of the mark scheme
- prepare well by thoroughly revising each topic in the specification (for example working capital is a concept that many learners struggle with)
- learners should prepare well by thoroughly revising each topic in the specification
general tips on calculations
- always complete calculations to 2 decimal places
- for calculation questions, it is advised that candidates show each stage of their workings - this enables marks to be awarded even if the final answer is incorrect
- in case you don't know the calculation - stating the correct formula could award you marks and show understanding
- with calculation questions, it is always a good idea to state the formula first
general tips for business essays (1/2)
- use an opening paragraph to explain what the key term means, followed by two paragraphs, each one assessing a one side of your argument
- Knowledge can be demonstrated by defining key terms at the beginning of a response
- arguments need to be well developed with coherent chains of reasoning and consistently supported by context
- use paragraphs in responses to make it clear that you are making a new point, especially if it is a contrasting argument
- to be fully balanced, a response needs to have complete chains of reasoning for both sides of an argument
- learners are expected to provide a final judgement and/or conclusion
- in evaluate questions, recommendations should be supported by quantitative or qualitative data
general tips for business essays (2/2)
- learners should be encouraged to make fewer arguments but to ensure that they are well developed and contextualised
- make use of theory to justify the overall recommendation
- be specific! for example learners are expected to focus on the usefulness of SWOT in terms of helping continued success, rather than a generic response on how SWOT can be used
- evaluate questions always require learners to provide a balanced response with arguments both for and against
- the concept of cash flow verses profit is a difficult one for many learners (read the evaluate question from previous section)